Algorithmic textures
Table of Contents
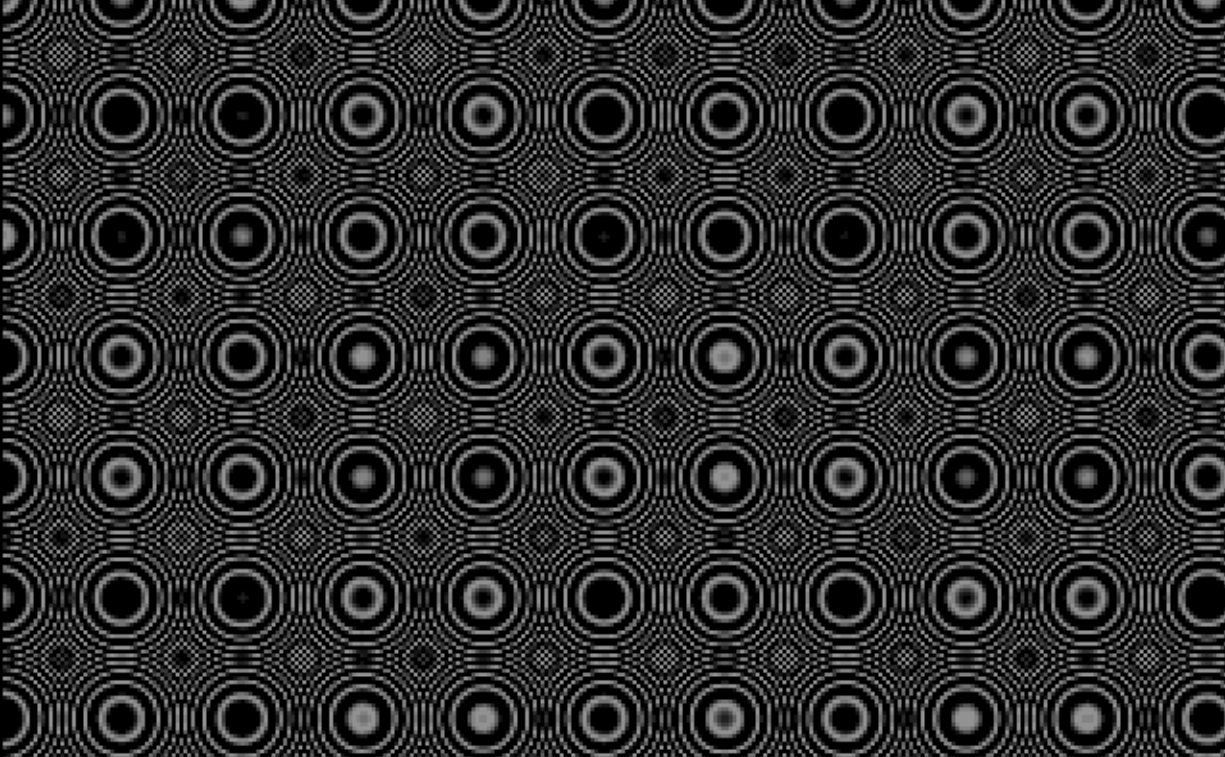
1. Circular waves
This QBasic program creates visually captivating circular wave patterns by manipulating pixel colors based on sine function calculations. It's a simple yet effective demonstration of how mathematical functions can be used to generate complex visual patterns.
The program uses two nested loops to iterate over each pixel on the screen. The outer loop handles the vertical axis (y-coordinate), and the inner loop handles the horizontal axis (x-coordinate).
For each pixel, the program calculates a sine value based on the squared distance from the origin (0,0). This calculation involves the formula:
colorvalue = SIN((x^2 + y^2) / 10) * 10
This program is a blend of mathematics and art, showcasing how simple algorithms can produce intricate and visually appealing results.
' Program to render circular wave patterns. ' Algorithm was accidentally discovered while experimenting with sine function. ' ' This program is free software: released under Creative Commons Zero (CC0) license ' by Svjatoslav Agejenko. ' Email: svjatoslav@svjatoslav.eu ' Homepage: http://www.svjatoslav.eu ' ' Changelog: ' 2003, Initial version ' 2025, Improved program readability SCREEN 13 ' Initialize the screen mode to 320x200 with 16 colors ' Outer loop for the vertical axis (y-coordinate) FOR ycoordinate = 1 TO 199 ' Inner loop for the horizontal axis (x-coordinate) FOR xcoordinate = 1 TO 319 ' Calculate the sine value based on the squared distances from the origin colorvalue = SIN((xcoordinate ^ 2 + ycoordinate ^ 2) / 10) * 10 ' Clamp the color value to the range [0, 15] IF colorvalue < 0 THEN colorvalue = 0 IF colorvalue > 15 THEN colorvalue = 15 ' Set the pixel color at (xcoordinate, ycoordinate) with an offset to use the full 16-color palette PSET (xcoordinate, ycoordinate), colorvalue + 16 NEXT xcoordinate NEXT ycoordinate ' Wait for user key press WHILE INKEY$ = "": WEND CLS END
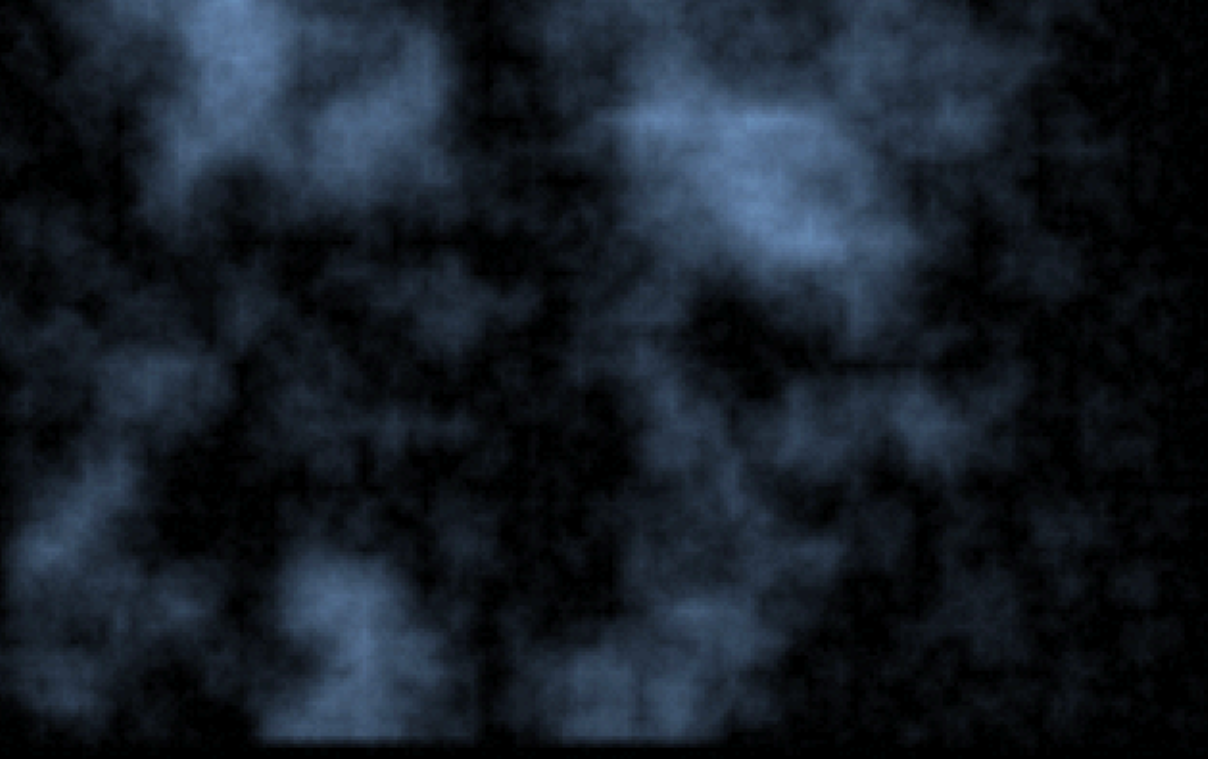
2. Diamond square clouds
This QBasic program demonstrates the Diamond-Square algorithm, a method used to generate fractal terrain or cloud surfaces. The algorithm is particularly useful for creating realistic landscapes or textures in computer graphics.
DECLARE SUB DrawPixels (x1 AS INTEGER, y1 AS INTEGER, s AS INTEGER) ' Program to render cloud surface using diamond square algorithm. ' ' This program is free software: released under Creative Commons Zero (CC0) license ' by Svjatoslav Agejenko. ' Email: svjatoslav@svjatoslav.eu ' Homepage: http://www.svjatoslav.eu ' ' Changelog: ' 2003.12, Initial version ' 2024.08, Improved program readability DECLARE SUB DrawBox (x1 AS INTEGER, y1 AS INTEGER, s AS INTEGER) DECLARE SUB SetPalette () DECLARE SUB InitializeProgram () DEFINT A-Z InitializeProgram DIM SHARED maxLightness AS INTEGER maxLightness = 127 DIM scale AS INTEGER scale = 2 ^ 8 1 : scale = scale \ 2 x1 = (319 \ scale) - 1 y1 = (199 \ scale) - 1 FOR y = 0 TO y1 FOR x = 0 TO x1 DrawPixels x * scale, y * scale, scale NEXT x NEXT y IF scale > 2 THEN GOTO 1 WAITa$ = INPUT$(1) SUB DrawPixels (x1 AS INTEGER, y1 AS INTEGER, s AS INTEGER) ' Get the lightness values for the corners of the box c1 = POINT(x1, y1) c2 = POINT(x1 + s, y1) c3 = POINT(x1, y1 + s) c4 = POINT(x1 + s, y1 + s) ' Calculate the midpoint lightness values sp = s \ 2 k = s * 2 kp = k / 2 cc2 = ((c1 + c2) / 2) + (RND * k) - kp IF cc2 > maxLightness THEN cc2 = maxLightness IF cc2 < 0 THEN cc2 = 0 cc3 = ((c1 + c3) / 2) + (RND * k) - kp IF cc3 > maxLightness THEN cc3 = maxLightness IF cc3 < 0 THEN cc3 = 0 cc4 = ((c2 + c4) / 2) + (RND * k) - kp IF cc4 > maxLightness THEN cc4 = maxLightness IF cc4 < 0 THEN cc4 = 0 cc5 = ((c3 + c4) / 2) + (RND * k) - kp IF cc5 > maxLightness THEN cc5 = maxLightness IF cc5 < 0 THEN cc5 = 0 ' Calculate the central lightness value cc1 = ((cc2 + cc3 + cc4 + cc5) / 4) + (RND * k) - kp IF cc1 > maxLightness THEN cc1 = maxLightness IF cc1 < 0 THEN cc1 = 0 ' Set the calculated lightness values for the box PSET (x1 + sp, y1 + sp), cc1 PSET (x1 + sp, y1), cc2 PSET (x1, y1 + sp), cc3 PSET (x1 + s, y1 + sp), cc4 PSET (x1 + sp, y1 + s), cc5 END SUB SUB InitializeProgram ' Set the screen mode and initialize the color palette SCREEN 13 SetPalette RANDOMIZE TIMER END SUB SUB SetPalette ' Set the color palette for lightness levels FOR a = 0 TO 255 OUT &H3C8, a OUT &H3C9, a / 4 OUT &H3C9, a / 3 OUT &H3C9, a / 2.3 NEXT a END SUB
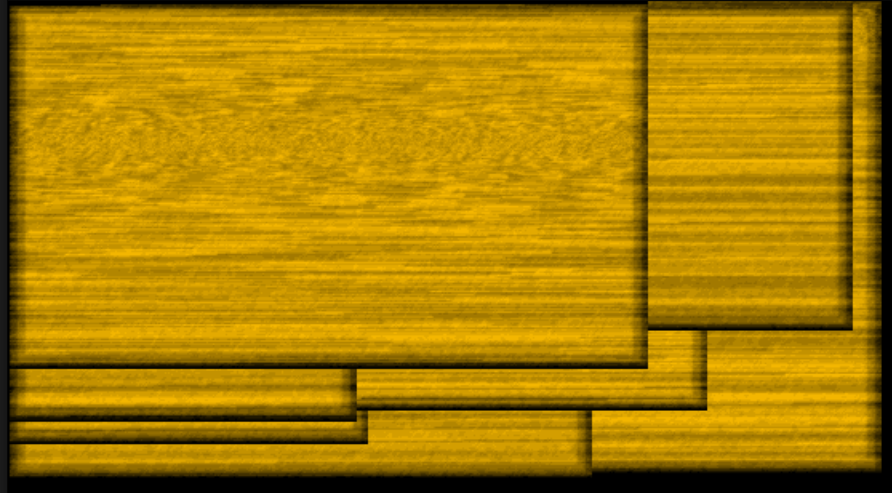
3. Old paper
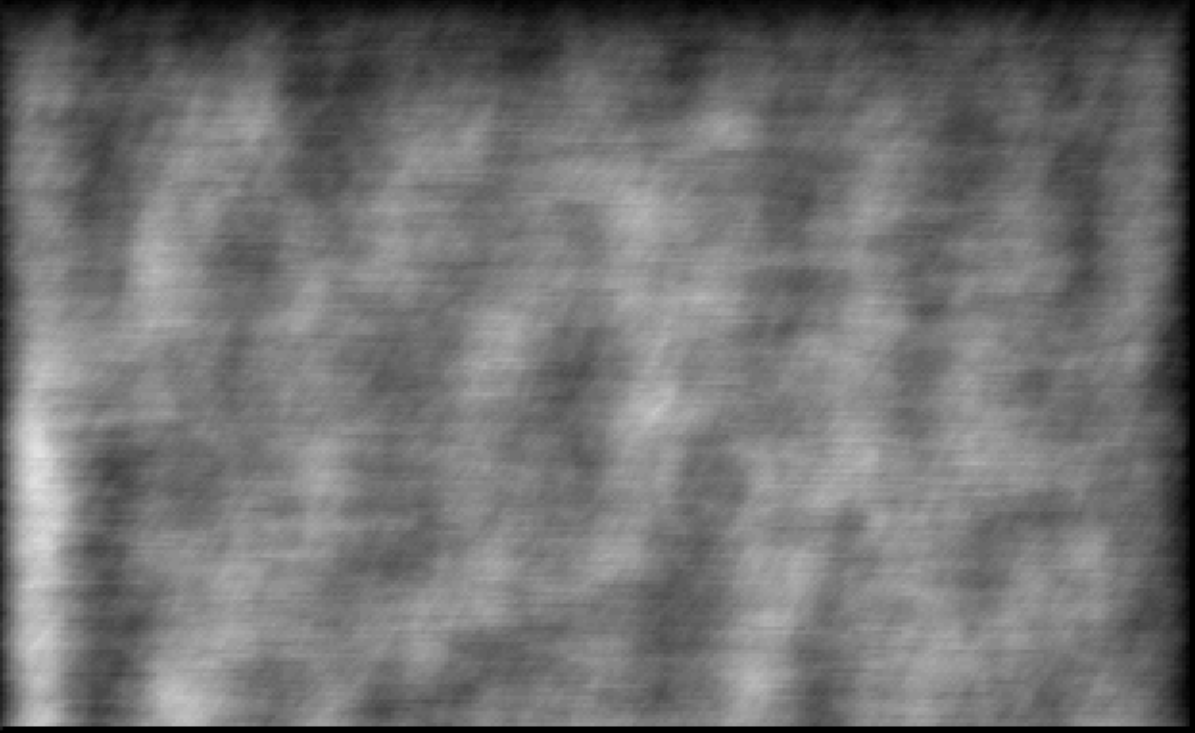
This QBasic program generates a procedural texture that simulates the appearance of old paper.
The program initializes the screen to a 320x200 resolution with 256 colors (SCREEN 13 in QBasic) and sets up a grayscale color palette. Each color index from 0 to 63 is assigned a shade of gray, creating a smooth gradient.
The program generates the texture by iterating over each pixel on the screen. For each pixel, it calculates a color value based on the color of the pixel directly above it, adding a small amount of random noise. This creates a smooth transition between pixels with controlled randomness, mimicking the fibrous texture of paper.
' Program to render surface resembling old paper. ' ' This program is free software: released under Creative Commons Zero (CC0) license ' by Svjatoslav Agejenko. ' Email: svjatoslav@svjatoslav.eu ' Homepage: http://www.svjatoslav.eu ' ' Changelog: ' 2003, Initial version ' 2025, Improved program readability DEFINT A-Z SCREEN 13 RANDOMIZE TIMER ' Initialize the color palette to grayscale. Each color index from 0 to 63 has R, G, B values equal to the index, ' creating a smooth grayscale gradient for the 256-color mode. FOR paletteIndex = 0 TO 63 OUT &H3C8, paletteIndex OUT &H3C9, paletteIndex ' Set red component OUT &H3C9, paletteIndex ' Set green component OUT &H3C9, paletteIndex ' Set blue component NEXT paletteIndex noiseOffset = 0 ' Generate a paper-like surface by averaging the color of the pixel above with some randomness. ' This creates a procedural texture that mimics the roughness of paper. FOR y = 1 TO 190 FOR x = 1 TO 310 stepCounter = stepCounter + 1 ' Approximately every 10 steps, introduce a new random noise offset to create variation in the pattern. ' This prevents the surface from becoming too uniform. IF stepCounter > 10 THEN noiseOffset = RND * currentColor / 20 stepCounter = stepCounter - (RND * 20 + 10) END IF ' Get the color of the pixel directly above the current position. topColor = POINT(x, y - 1) ' Calculate the current color as the average of the top color and the previous current color, ' plus a small random noise and minus the noise offset. This creates a smooth transition with ' controlled randomness. currentColor = (topColor + currentColor) \ 2 + ((RND * 2) - noiseOffset) ' Clamp the color value to stay within the valid palette range (0 to 63). IF currentColor < 0 THEN currentColor = 0 IF currentColor > 63 THEN currentColor = 63 ' Plot the current pixel at (x-1, y) using the calculated color. PSET (x - 1, y), currentColor NEXT x ' Set the starting color for the next row to the last calculated color of the current row. ' This ensures continuity between rows. PSET (0, y + 1), currentColor NEXT y ' Wait for a single key press before exiting the program. inputKey$ = INPUT$(1) SYSTEM
4. Wood
This QBasic program creates a visually appealing simulation of a wood surface. It is designed to generate a realistic wood grain texture using simple graphical techniques.
' Program to render surface resembling wood. ' ' This program is free software: released under Creative Commons Zero (CC0) license ' by Svjatoslav Agejenko. ' Email: svjatoslav@svjatoslav.eu ' Homepage: http://www.svjatoslav.eu ' ' Changelog: ' 2003.12, Initial version ' 2024 - 2025, Improved program readability DECLARE SUB DrawWoodSurface (woodX%, woodY%) DECLARE SUB DrawPaper (xPos%, y1Pos%) DEFINT A-Z SCREEN 12 RANDOMIZE TIMER ' Set palette colors FOR colorIndex = 0 TO 15 OUT &H3C8, colorIndex OUT &H3C9, colorIndex * 4 OUT &H3C9, colorIndex * 3 OUT &H3C9, colorIndex * 0 NEXT colorIndex ' Main loop to draw wood at random positions 100: woodX = RND * 400 + 200 woodY = RND * 100 + 200 CALL DrawWoodSurface(woodX, woodY) GOTO 100 ' Wait for user input to exit exitKey$ = INPUT$(1) SUB DrawWoodSurface (woodX, woodY) DIM lowerY AS INTEGER DIM phaseOffset AS INTEGER DIM xStepCounter AS INTEGER DIM randomOffset AS INTEGER DIM newColor AS INTEGER DIM upperColor AS INTEGER DIM currentColor AS INTEGER ' Draw the outline of the wood lowerY = woodY + 1 LINE (0, 0)-(woodX, woodY), 0, BF ' Black background LINE (5, 5)-(woodX - 5, lowerY - 5), 8, BF ' Gray wood outline LINE (10, 10)-(woodX - 10, lowerY - 10), 15, BF ' White inner highlight ' Initialize random phase offset for color variation phaseOffset = RND * 300 ' Draw the wood texture FOR y = woodY - 1 TO 0 STEP -1 FOR x = woodX - 1 TO 0 STEP -1 xStepCounter = xStepCounter + 1 IF xStepCounter > woodX THEN randomOffset = RND * 13 ' Small random noise for texture variation xStepCounter = SIN((y + phaseOffset) / 100) * woodX ' Sine wave to create wavy grain pattern END IF upperColor = POINT(x, y + 1) ' Get color from upper pixel currentColor = POINT(x, y) ' Get color from current pixel newColor = (upperColor * 2 + currentColor + newColor * 3 + randomOffset) / 7 + RND * 1 ' Ensure color value is within the valid range (0-15) IF newColor < 0 THEN newColor = 0 IF newColor > 15 THEN newColor = 15 ' Set the pixel color for the wood texture PSET (x + 1, y), newColor NEXT x NEXT y END SUB
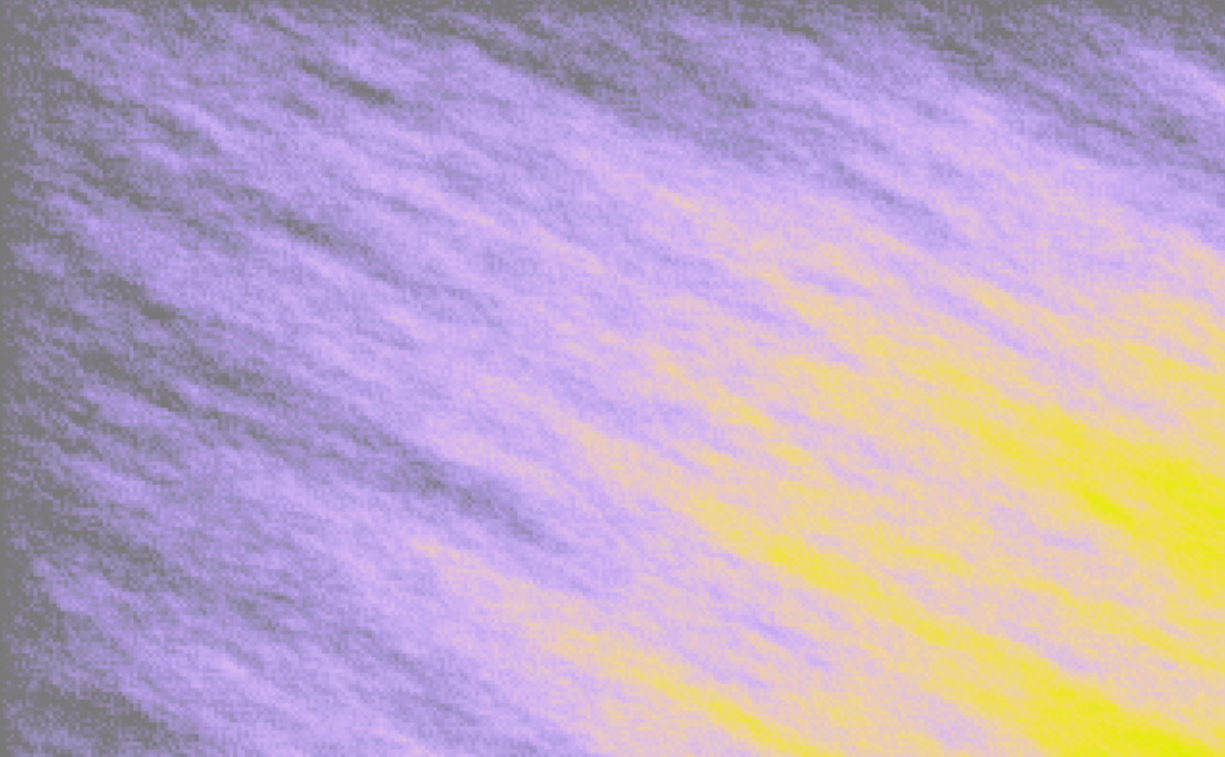
5. Yellow flame
"Yellow Flame" is a visually captivating program written in QBasic that generates a dynamic flame-like pattern on the screen.
Program initializes the color palette using sine waves to create a smooth gradient of colors. This gradient is essential for the flame effect.
The core of the program involves generating a surface pattern that mimics a flame. It does this by iterating over each pixel on the screen and calculating the average color of the surrounding pixels. A small amount of randomness is added to this average to create a natural, flickering effect.
' Yellow flame. ' ' This program is free software: released under Creative Commons Zero (CC0) license ' by Svjatoslav Agejenko. ' Email: svjatoslav@svjatoslav.eu ' Homepage: http://www.svjatoslav.eu ' ' Changelog: ' 2003.12, Initial version ' 2024.08, Improved program readability DEFINT A-Z ' Define all variables as integers SCREEN 13 ' Set graphics mode to 320x200 with 256 colors RANDOMIZE TIMER ' Seed the random number generator ' Initialize palette registers with sine wave colors FOR paletteIndex = 0 TO 255 OUT &H3C8, paletteIndex OUT &H3C9, INT(SIN(paletteIndex / 21) * 30 + 30) OUT &H3C9, INT(SIN(paletteIndex / 34) * 30 + 30) OUT &H3C9, INT(SIN(paletteIndex / 10) * 30 + 30) NEXT paletteIndex ' Generate the surface pattern FOR y = 1 TO 199 FOR x = 1 TO 319 prevPixel = POINT(x, y - 1) leftPixel = POINT(x - 1, y) diagPixel = POINT(x - 1, y - 1) left2Pixel = POINT(x - 2, y) ' Calculate the average of surrounding pixels and add some randomness newColor = (prevPixel + leftPixel + diagPixel + left2Pixel) \ 4 + (RND * 5 - 2) ' Clamp the color value within the valid range IF newColor < 0 THEN newColor = 0 IF newColor > 63 THEN newColor = 63 ' Set the pixel with the calculated color PSET (x, y), newColor NEXT x NEXT y ' Wait for user input to exit userInput$ = INPUT$(1)