Data over analog audio
Table of Contents
1. msg2xi: Text to Sound Encoder
msg2xi is a utility designed to encode arbitrary text messages into an 8-bit sound file. This program allows users to convert digital data into analog audio signals, making it possible to transmit text messages over traditional analog mediums such as telephone lines or magnetic tapes.
How It Works: The program reads text from an input file, processing it byte by byte. Each byte is broken down into its constituent bits. For each bit, a sine wave is generated. Different waveforms represent '1's and '0's (implementing frequency modulation). The generated waveforms are combined into a single audio file, encoding the original text message. A special pure sinewave header tone is added to the beginning of the audio file to mark the start of the encoded message, facilitating synchronization during decoding.
Download source code: Source code
2. xi2msg: Sound to Text Decoder
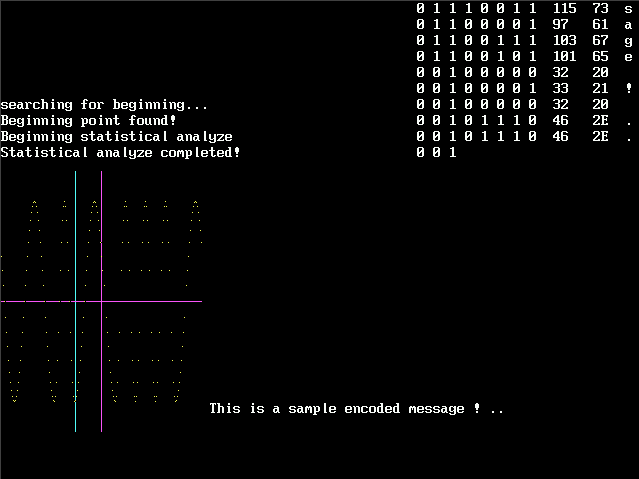
The xi2msg utility is designed to decode digital information from an audio file, specifically an 8-bit sound file. This program is part of a suite of utilities that enable the transmission of digital data over analog audio mediums, such as telephone lines or magnetic tapes.
The xi2msg utility works by analyzing the audio file to locate peaks between waveforms. It calculates the distance between these peaks to determine whether each segment represents a '0' or a '1' bit. This process involves several key steps:
- Header Detection
- The program starts by searching for a special header tone in the audio file. This header tone marks the beginning of the encoded message and helps synchronize the decoding process.
- Peak Analysis
- The utility measures the distance between peaks in the audio waveform. Long distances between peaks are interpreted as '0' bits, while short distances are interpreted as '1' bits.
- Bit Assembly
- The detected bits are sequentially assembled into bytes. Each byte is then converted into its corresponding character.
- Output
- The decoded message is displayed on the screen and written to an output file, making it accessible for further use or analysis.
The program relies on frequency modulation for decoding data, which was chosen for its resilience to amplitude distortions that can occur during analog transmission. This makes the utility particularly effective for decoding messages recorded on cassette tapes or transmitted over telephone lines.
Download source code: Source code
3. aver
The aver.bas utility is designed to reduce noise in digitized audio files by smoothing out noise peaks, which is particularly beneficial for audio files transmitted over analog mediums like telephone lines or magnetic tapes, where noise interference is common.
The program starts by asking the user for two critical factors: the averaging factor and the divide factor. These parameters determine the intensity of the noise reduction applied.
For each byte read from the input file, the program stores the last N values (where N is the averaging factor). These values are averaged, and the result is scaled by the divide factor. This averaging technique helps to smooth out noise spikes in the audio data.
The program provides a graphical representation of the original and smoothed audio. This allows for visual comparison of the original and processed signals on the screen. The smoothed audio data is written to an output file, which should have reduced noise compared to the input file.
The program uses command-line input to determine the filenames for input and output, defaulting to appending .awe to the input filename for the output file.
Download source code: Source code